Bake ambient occlusion
API functions:
Ambient occlusion (AO) is a rendering technique increasing realism by simulating real-world shadowing. To limit the computational cost in your real time application, you can precompute the self occlusion of an object, and store these values to a dedicated texture.

Computation
Similarly to any other map baking, ambient occlusion can be baked thanks to the dedicated function algo.bakeAOMap called within a session lifecycle:
sessionId = algo.beginBakingSession(destinations, sources, 0, 1024)
aoMaps = algo.bakeAOMap(sessionId, samples = 32)
algo.endBakingSession(sessionId)
Occlusions are detected by ray tracing, where the number of rays cast for each texel is given by the parameter samples. This is the only map baking function for which the biggest part of the computation load is not held by algo.beginBakingSession, but by the function itself, due to these additional rays.
Warning
Note that the set of values accepted by the parameter samples are powers of two in the range [8, 4096]. Any other value will trigger an exception.
Depending on the required map resolution and number of samples, ambient occlusion computation can be time consuming. It is strongly recommended, if possible, to enable the GPU back-end for this operation.
Note however that samples are generated so as to ensure a blue noise distribution of the error in texture space, which has pretty nice properties:
- error is scattered in such a way that it is perceptually less significant,
- it shows good behaviour with respect to smoothing (see Filtering).
This allows to get good quality results, even with quite a few samples.
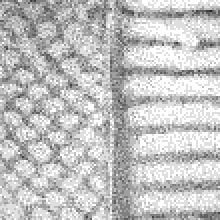
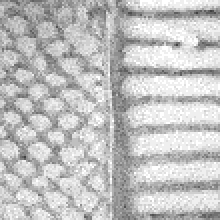
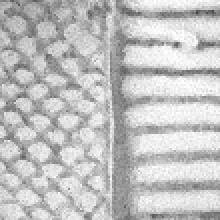
The figure below shows the impact of blue noise on AO baking results for different sample counts per pixel (spp):
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|
| 8 spp | 16 spp | 32 spp |
Bent normals
The bent normal at a given surface point corresponds to the axis of the cone defined by non-occluded directions. It is used by some rendering engines for advanced shadowing techniques.
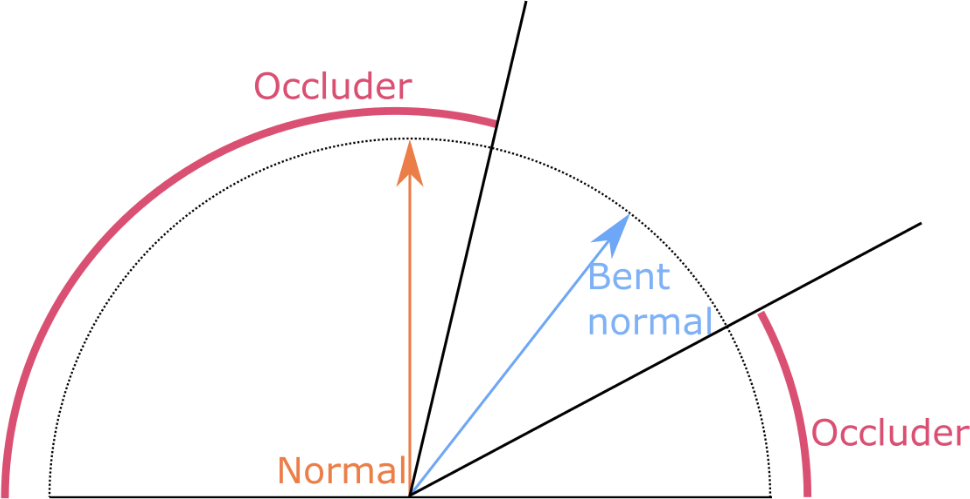
Bent normals are usually computed contemporaneously with ambient occlusion, thus avoiding additional cost. This is why there is no dedicated function to bake them, but just a flag in the algo.bakeAOMap function:
aoMaps = algo.bakeAOMap(sessionId, samples = 32, bentNormals = True)
If the flag is enabled, the returned list contains both AO and bent normal maps, stored in an interleaved manner:
aoMaps[0]: first AO mapaoMaps[1]: first bent normal mapaoMaps[2]: second AO mapaoMaps[3]: second bent normal map- ...
Filtering
To get a smoother result without requiring to drastically increase the number of samples, the ambient occlusion map can be filtered by using function material.filterAO, which preserves signal discontinuities by combining three Gaussian blurs, respectively depending on:
- texel coordinates (controlled by parameter
sigmaPos), - ambient occlusion values (controlled by parameter
sigmaValue), - normal orientations (controlled by parameter
sigmaNormal).
The higher the sigma value, the stonger the related blur (see this paper for more details).
The third criterion requires a normal map to be provided to the function as well. The code below shows a classic usage of AO filtering:
sessionId = algo.beginBakingSession(destinations, sources, 0, 1024)
normalMaps = algo.bakeNormalMap(sessionId)
aoMaps = algo.bakeAOMap(sessionId, samples = 32)
algo.endBakingSession(sessionId)
filteredAO = material.filterAO(aoMaps, normalMaps) # apply filter with default values.
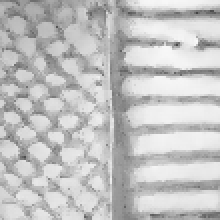
The following image illustrates the effect of each component of the filter:
 |
 |
 |
 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 16 spp No filtering |
sigmaPos = 2 |
sigmaPos = 2, sigmaValue = 0.2 |
sigmaPos = 2, sigmaValue = 0.2, sigmaNormal = 0.2 |
Filtering along positions only is equivalent to applying a Gaussian smoothing to the texture. As expected, most of the details are lost. Combining it with value filtering makes the result looks like the one of a bilateral filter. Together with normal filtering, it allows to remove noise from the texture while preserving its most salient features.